Ankle Started Bruising Again After Sprained
Ankle Sprain Handling
Early Ankle Sprain Treatment can help to speed recovery and minimize the symptoms. Hither are a few simple treatment steps to follow for sprained ankle. For better understanding of Ankle Sprain Treatment, lets start empathise-
What is Ankle Sprain?
An Ankle sprain is actually an injury to the ligaments of the ankle joint, which are rubberband, band-like structures that hold the bones of the ankle articulation together and prevent excess turning and twisting of the joint. In normal movement, the ligaments tin stretch slightly and then retract dorsum to their normal shape and size. A sprain results when the ligaments of the ankle accept been stretched across their limits. In severe sprains, the ligaments may be partially or completely torn.
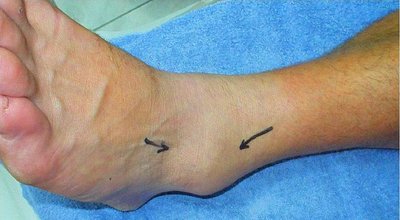
The ankle joint is fairly unstable and largely depends on the ligaments for its stability. The ankle sprain is of ii types-
- one-Pronation or eversion type.
- 2-Supination and inversion type.
The virtually common type is theinversion ankle sprain (85%), in which the ankle rolls over on the outside. In the sprained talocrural joint the most common damage is washed to the talo-fibula ligament (if the talocrural joint sprain is worse, the calcaneo-fibula ligament can also be damaged) - sometimes the tendons also become damaged.
Mechanism of Talocrural joint sprain
The ligament is injured when theplantar flexed foot is suddenly forced into inversion, which may cause rupture, sprain of lateral ligament.
The injury is common in sports activity. It is quite common when a person slips off or walk on uneven surfaces. The foot is forced into inversion and plantar flexion which results in external rotation of tibia. The site of injury is more often than not the centre and distal attachments of anterior and heart band of the ligament.
When sudden inversion force occurs with the talocrural joint in mid position of dorsi and plantar flexion, the injury involves the calcaneo-fibular ligament(CFL). Whereas when the excessive inversion-adduction movement is associated with forced plantar flexion, the injury commonly involvesanterior talo-fibular ligament(ATFL). This can exist identified by the site of pain and tenderness. Pain and tenderness over talus indicates injury to talo-fibular ligament while the aforementioned over calcaneus indicates the involvement of calcaneo-fibular ligament. This identification is necessary for prompt handling.
Sprained ankle is oft classified equally
First caste ankle sprain- Some stretching or balmy trigger-happy of the ligament.- Piffling or no functional loss - the joint can notwithstanding function and bear some weight (...but hurts!!!).- Balmy pain-Some swelling- Some joint stiffness- Render to activity/functional phase in i-two weeks with proper ankle sprain treatment.
2d degree talocrural joint sprain:- Some more than severe tearing of the ligaments-Moderate instability of the joint- Moderate to astringent pain - weight-bearing is very painful- Swelling and stiffness- Return to activity/functional phase in 2-iii weeks with proper treatment.
Third caste ankle sprain:- Total rupture of a ligament - at that place is a loss of motion-Gross instability of the joint - articulation function is lost-Severe pain initially followed by no pain- Severe swelling- Usually extensive bruising- Render to activity/functional phase in 3-half dozen weeks with proper ankle sprain treatment.
Risk factors predisposing to ankle sprains:
- -poor rehabilitation of a previous sprained ankle
- -poor proprioception (proprioception is the ability to sense where a articulation is .... if you lot don't know where your ankle is, the muscles will not be able to prevent the ankle sprain)
- -some feet are very easy to 'tip over' - this is mutual in those who oft 'roll the ankle', without actually doing any damage and spraining the ankle
- -weak muscles (they are only not strong plenty to prevent the sprain occurring)
- -Use of high heels.
Sprained Ankle Symptoms
- History-The patient describes 'going over' at the ankle.
- Pain- There is sharp pain just below and anterior to the lateral malleolus. Passive stretching and weight begetting increase the pain. Pain because the nerves are more sensitive: The joint hurts and may throb.
- Swelling- When an ankle is injured with a sprain, tissue injury and the resulting inflammation occur. Blood vessels become "leaky" and allow fluid to ooze into the soft tissue surrounding the joint. White claret cells responsible for inflammation migrate to the surface area, and blood period increases also. This is present from the lateral edge of tendo-achilles, over the lateral malleolus along the dorsum of the foot. In astringent injuries, swelling may spread to the back of the toe and upward to the leg.
- Bruising- This appears under the lateral malleolus and over the dorsum of the foot.
- Loss of function- All weight bearing is painful, then the patient cannot run and has a gait with a very short stance phase on the afflicted pes.
Concrete examination of Ankle
Concrete test reveals mild swelling in form ane sprains and moderate to severe swelling in a diffuse pattern in grade two and iii sprains. Tenderness is usually elicited at the inductive border of the fibula with ATFL injuries and at the tip of the fibula with CFL injuries. The region of the syndesmosis and the base of operations of the fifth metatarsal should likewise be palpated to rule out injuries to these structures.Once proper physical examination and diagnosis is done Ankle sprain Treatment can be started.
The Inductive drawer test and the Talar tilt test are commonly used to identify signs of joint instability. The Anterior drawer test is performed by stabilizing the distal tibia anteriorly with one hand and pulling the slightly plantar flexed foot forward with the other mitt from behind the heel. A positive finding of more than 5 mm of inductive translation indicates a tear of the ATFL. The Talar tilt test is performed by stabilizing the distal tibia with ane hand and inverting the talus and calcaneus every bit a unit of measurement with the other hand. A positive finding of more than than 5 mm with a soft endpoint indicates a combined injury to the ATFL and CFL. Information technology is important to always compare the affected ankle with the contra lateral side because some patients are naturally very flexible (generalized ligament laxity), and this could effect in false positive examination.
Differentiating between a sprained ankle and an talocrural joint fracture can be difficult, and sometimes anten-ray is needed.
Examination of the Talocrural joint subsequently an inversion injury
A good thorough test of ankle joint is necessary for Ankle Sprain Handling, which include-
- -Palpation of thelateral collaterals (ATFL and CFL)
- -Medial palpation of thedeltoid ligament
- -Palpation of the proximal fibula close to the knee to dominion out aMaisonneuve fracture (tearing of the interosseous membrane and proximal fibula fracture).
- -Squeeze test to rule out talocrural joint syndesmosis tearing with resultant ankle mortise instability.
- -Palpation of proximal (base) fifth metatarsal to dominion outavulsion fracture from peroneus brevis pull.
- -Anterior drawer and inversion (talar tilt) stress testing.
- -External rotation (Cotton wool) exam to examination for syndesmosis injury.
- -Motor testing of posterior tibial (inversion) and peroneal (eversion) tendons.
Ankle Sprain Handling
Astute Stage- Ankle Sprain Treatment
- -Grade ane sprain: 1-3 days
- -Grade two sprain: 2-4 days
- -Grade 3 sprain: 3-7 days
Goals-Acute Stage-Ankle Sprain Treatment
Decrease pain and swelling, protect from re injury and maintain appropriate weight begetting condition.
PRICE
- i) Protection Options Taping, functional bracing, removable bandage boot (grade2 and 3 sprains)
- two) Rest (crutch to promote ambulation).
- three) Ice Cryocuff ice machine, ice bags, ice with other modalities (interferential , ultrasound, loftier-voltage galvanic stimulation).
- 4) Compression Rubberband wrap, TED hose, Vaso-pneumatic pump.
- 5) Elevation In a higher place heart level with ankle pump.
Sub-Acute Phase- Ankle Sprain Treatment
- -Grade 1 sprain: 2-iv days
- -Grade 2 sprain: 3-five days
- -Grade 3 sprain: 4-8 days
Goals-Sub-Acute Phase-Ankle Sprain Treatment
Decrease pain and swelling, increase pain costless range of motion, begin strengthening, begin non-weight bearing proprioceptive training and provide protective support as needed.
1) Modalities to decrease pain and swelling
- -Water ice and dissimilarity baths
- -Electrical stimulation (loftier-voltage galvanic or interferential)
- -Ultrasound
- -Cross-friction massage(gently)
- -Soft orthotics with 1/8-three/sixteen inch lateral wedge, if needed in Ankle Sprain Treatment.
ii) Weight bearing
Progress weight begetting as symptoms permit. Partial weight bearing to total weight bearing if no signs of antalgic gait is nowadays.
three) Physiotherapy exercises for ankle sprain
- -Agile range of movement exercises- Dorsiflexion, inversion, foot circle, plantarflexion, eversion, alphabet.
- -Strength exercises- Isometrics in pain free range, toe curls with towel (place weight on towel to increase resistance). Choice up objects with toes (tissue, marble).
- -Proprioceptive grooming- Seated Biomechanical Talocrural joint Platform Arrangement (BAPS). Wobble board. Ankle disc.
- -Stretching- Passive ROM- only dorsi flexion and plantar flexion in pain free range. No eversion or inversion even so. Achilles stretch. Joint mobilization (class ane-2 for dorsiflexion and plantarflexion).
Rehabilitative Stage- Ankle Sprain Treatment
- -Form 1 sprain:1 week
- -Grade 2 sprain:two week
- -Grade 3 sprain:3 week
Goals- Rehabilitative Stage- Ankle Sprain Treatment
Increase hurting-gratis ROM. Progress strengthening. Progress proprioceptive training. Increase hurting-free activities of daily living. Pain-gratuitous full weight bearing and uncompensated gait.
1) Therapeutic exercises for ankle sprain
- -Stretching- of gastrocnemius and soleus with increased intensity. Joint mobilization (grades 1,2 and 3 for dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, and eversion, hold inversion).
- -Strengthening- Weight bearing exercises. Heel raises. Toe raises. Stair steps. Quarter squats.
- Concentric/Eccentric and isotonics (theraband and weight gage exercises) for inversion, eversion, plantar flexion, dorsi flexion, peroneal strengthening.
- -Proprioceptive grooming( Progress from non-weight bearing to controlled weight bearing to full weight bearing). Standing BAPS board. Standing wobble board. Single leg residuum activities (Stable to unstable surfaces, without to with distractions). Proprioceptive preparation has a major role in Ankle Sprain Handling.
2) Continue modalities equally needed, specifically after exercise to prevent re occurrence of pain and swelling.
3) Taping, Bracing and orthotics used as needed. To avert re injury.
Render to Action stage- Ankle Sprain Treatment
- -Grade ane sprain: 1-2 week
- -Grade 2 sprain: 2-three week
- -Course 3 sprain: 3-6 week
Goals- Return to Activity stage- Ankle Sprain Treatment
Regain full strength. Normal biomechanics. Return to participation. Protection and strengthening of whatsoever mild residual articulation instability.
i) Therapeutic exercises
Go along progression of ROM and strengthening exercises. Sports specific strengthening and training.
2) Running progression
- Unloaded jogging. Unloaded running. Alternate jog-walk-jog on smooth straight surfaces. Alternate sprint-jog-dart on smooth straight surfaces. Figure of eight drills. Zig-zag cutting.
- Agility drills like back pedaling, side stepping, Carioca.
- Plyometrics specific to each sport.
- Progress weight bearing multi directional residue exercises and movement activities.
Further Reading
- Ankle Sprain. The American Orthopaedic Pes & Talocrural joint Social club (AOFAS)
- Ankle Sprain. eMedicineHealth
- Ankle Sprain. American College of Human foot and Ankle Surgeons (ACFAS)
- Sprained talocrural joint. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Sprained Ankle. OrthoInfo
- Fong DT, Hong Y, Chan LK, Yung PS, Chan KM. A systematic review on ankle injury and ankle sprain in sports. Sports Med. 2007;37(1):73-94.
- Kemler E, van de Port I, Backx F, van Dijk CN. A systematic review on the handling of astute ankle sprain: caryatid versus other functional treatment types. Sports Med. 2011 Mar 1;41(3):185-97.
- Chung-Wei Christine Lin, Claire Eastward Hiller, and Rob A de Bie. Evidence-based handling for ankle injuries: a clinical perspective. J Man Manip Ther. Mar 2010; 18(1): 22–28.
Return from Talocrural joint Sprain Treatment to sports physical therapy
Return from Ankle Sprain Handling to home folio
- Home
-
Web log & News
- What'southward New
- Physiotherapy News
-
Branches
- Neuro Rehab
- Ortho Physiotherapy
- Sports Physiotherapy
- Chest Physiotherapy
- Skin Disorders
- PT For Women
- Pediatric Physiotherapy
- Weight Loss Exs
- Hydrotherapy Exs
- Geriatric Rehab
-
Links
- Physiotherapy Links
- Contact United states of america
Source: https://www.physiotherapy-treatment.com/ankle-sprain-treatment.html